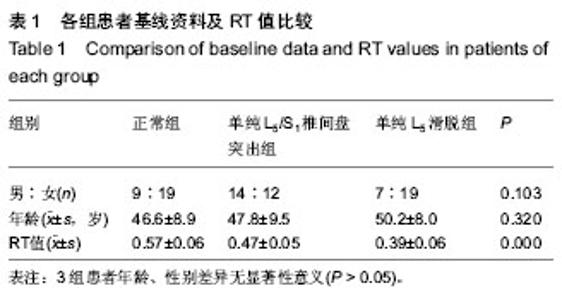
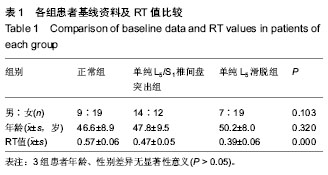
| [1] 杜心如,张一模. 髂腰韧带的形态及其临床意义[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志, 1995, 13(3): 221-223.
[2] 张国川,张英译,宋朝晖,等.髂腰韧带的形态及抗L5椎体滑脱的生物力学研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2007,25(1):85-87.
[3] Luk KD, Ho HC, Leong JC. The iliolumbar ligament. A study of its anatomy, development and clinical significance. J Bone Joint Surg. 1986;68(2): 197-200.
[4] Viehöfer AF, Shinohara Y, Sprecher CM, et al. The molecular composition of the extracellular matrix of the human iliolumbar ligament. Spine J. 2013. pii: S1529-9430(13)01445-9.
[5] Aihara T, Takahashi K, Ogasawara A, et al. Intervertebral disc degeneration associated with lumbosacral transitional vertebrae: a clinical and anatomical study. J Bone Joint Surg. 2005;87(5): 687-691.
[6] Ohmori K, Ishida Y, Takatsu T, et al. Vertebral slip in lumbar spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. Long-term follow-up of 22 adult patients. J Bone Joint Surg. 1995;77(5): 771-773.
[7] 栾兴胜,刘宝良,李宝兰. CT与X线观测慢性下腰痛患者腰椎曲度变化研究[J].中国煤炭工业医学杂志,2005,8(8): 825-826.
[8] 陈进军,唐华平,陈武.腰椎间盘突出与腰大肌横断面积关系的CT探讨[J].中国现代医学杂志,2003,13(4):45-47.
[9] 王春.腰椎间隙高度测量的临床意义[J].颈腰痛杂志,1994,15(4): 203-204.
[10] 卓启瑶,黄友锦,丁忠平,等.下腰椎关节突关节的CT诊断[J].现代医用影像学,2005,14(1):37-38.
[11] 王玉明,陈仲强,党耕町.腰椎黄韧带的退行性改变及相关因素[J].内蒙古医学杂志,2001,33(3):263-269.
[12] 李海. 腰椎棘间韧带退行性改变的组织学观察与腰椎间盘突出症发病关系的研究[D].山东中医药大学, 2004.
[13] Nazarian S. Spondylo1isthesis and spondylolytic spondylolithesis. A review of current concepts on pathogenesis, history,clinical symptoms imaging and therapeutic management. Eur Spine J. 1992;1(2):62-83.
[14] Hanson DS, Bridwell KH, Rhee JM, et al. Correlation of pelvic incidence with low-and high-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis. Spine. 2002;27(18): 2026-2029.
[15] Labelle H, Roussouly P, Berthonnaud É, et al. Spondylolisthesis, pelvic incidence, and spinopelvic balance: a correlation study. Spine. 2004;29(18): 2049-2054.
[16] Curylo LJ, Edwards C, DeWald RW. Radiographic markers in spondyloptosis: implications for spondylolisthesis progression. Spine. 2002;27(18): 2021-2025.
[17] Grobler LJ, Robertson PA, Novotny JE, et al. Etiology of spondylolisthesis: assessment of the role played by lumbar facet joint morphology. Spine. 1993;18(1): 80-91.
[18] Boden SD, Riew KD, Yamaguchi K, et al. Orientation of the Lumbar Facet Joints: Association with Degenerative Disc Disease. J Bone Joint Surg. 1996;78(3): 403-411.
[19] Dai LY. Orientation and tropism of lumbar facet joints in degenerative spondylolisthesis. Int Orthop. 2001;25(1): 40-42.
[20] SATO K, WAKAMATSU E, YOSHIZUM A, et al. The configuration of the laminas and facet joints in degenerative spondylolisthesis: a clinicoradiologic study. Spine. 1989; 14(11): 1265-1271.
[21] Barrey C, Jund J, Perrin G, et al. Spinopelvic alignment of patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis. Neurosurgery. 2007;61(5): 981-986.
[22] Okuda T, Baba I, Fujimoto Y, et al. The pathology of ligamentum flavum in degenerative lumbar disease. Spine. 2004;29(15): 1689-1697.
[23] Ono K, Yonenobu K, Miyamoto S, et al. Pathology of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament and ligamentum flavum. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;359: 18-26.
[24] Gruber HE, Hoelscher G, Ingram JA, et al. Immunolocalization and Biochemical Evidence of Pregnancy-Associated Plasma Protein-A in the Intervertebral Disc. Spine. 2008;33(14): E447-E454.
[25] Imada K, Matsui H, Tsuji H. Oophorectomy predisposes to degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg. 1995;77(1): 126-130.
[26] Sengupta DK, Herkowitz HN. Degenerative spondylolisthesis: review of current trends and controversies. Spine. 2005;30 (6S): S71-S81.
[27] Uhthoff HK. Prenatal development of the iliolumbar ligament. J Bone Joint Surg. 1993;75(1): 93-95.
[28] Hanson P, Sonesson B. The anatomy of the iliolumbar ligament. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1994;75(11): 1245-1246.
[29] Leong JCY, Luk KDK, Chow DHK, et al. The biomechanical functions of the iliolumbar ligament in maintaining stability of the lumbosacral junction. Spine. 1987;12(7): 669-674.
[30] Farfan HF, Osteria V, Lamy C. The mechanical etiology of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976;117: 40-55.
[31] Saraste H, Broström LÅ, Aparisi T. Prognostic radiographic aspects of spondylolisthesis. Acta Radiologica Diagnosis (Sweden). 1984;25(5): 427-432.
[32] 刘国彬.成年男性髂腰韧带的解剖学测量及其与腰5椎体滑脱之间的生物力学研究[D].石家庄:河北医科大学, 2007.
[33] Basadonna PT, Gasparini D, Rucco V. Iliolumbar ligament insertions: in vivo anatomic study. Spine. 1996;21(20): 2313-2316.
[34] Rucco V, Basadonna PT, Gasparini D. ANATOMY OF THE ILIOLUMBAR LIGAMENT: A Review of its Anatomy and a Magnetic Resonance Study. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 1996; 75(6): 451-455.
[35] Hartford JM, McCullen GM, Harris R, et al. The iliolumbar ligament: three-dimensional volume imaging and computer reformatting by magnetic resonance: a technical note. Spine. 2000;25(9): 1098-1103.
[36] Fujiwara A, Tamai K, Kurihashi A, et al. Relationship between morphology of iliolumbar ligament and lower lumbar disc degeneration. J Spinal Disord. 1999;12(4): 348-352.
[37] Aihara T, Takahashi K, Yamagata M, et al. Does the iliolumbar ligament prevent anterior displacement of the fifth lumbar vertebra with defects of the pars? J Bone Joint Surg. 2000; 82(6): 846-850.
[38] Aihara T, Takahashi K, Ono Y, et al. Does the morphology of the iliolumbar ligament affect lumbosacral disc degeneration? Spine. 2002;27(14): 1499-1503.
[39] 王永峰,靳安民,汤善华,等.腰5峡部裂合并不同椎间节段退行变与髂腰韧带的关系[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2006, 24(1): 104-106.
[40] 李岩,崔泳,陆培农,等.腰椎峡部不连和滑脱 X 线平片横突结构测量及其临床意义[J].广东医学, 2010, 31(11): 1453-1454. |